Activity 1: Simple Light to Voltage Sensor
Imagine that your BOE Shield-Bot is navigating a course, and there’s a bright light at the end. Your robot’s final task in the course is to stop underneath that bright light. There’s a simple phototransistor circuit you can use that lets the Arduino know it detected bright light with a binary‑1, or ambient light with a binary-0. Incandescent bulbs in desk lamps and flashlights make the best bright-light sources. Compact fluorescent and LED light sources are not as easy for the circuit in this activity to recognize.
Ambient means ‘existing or present on all sides’ according to Merriam Webster’s dictionary. For the light level in a room, think about ambient light as the overall level of brightness.
Parts List
(1) phototransistor
(2) jumper wires
(1) resistor, 2 kΩ (red-black-red)
(1) incandescent or fluorescent flashlight or desk lamp
After some testing, and depending on the light conditions in your robotics area, you might end up replacing the 2 kΩ resistor with one of these resistors, so keep them handy:
(1) resistor, 220 Ω (red-red-brown)
(1) resistor, 470 Ω (yellow-violet-brown)
(1) resistor, 1 kΩ (brown-black-red)
(1) resistor, 4.7 kΩ (yellow-violet-red)
(1) resistor, 10 kΩ (brown-black-orange)
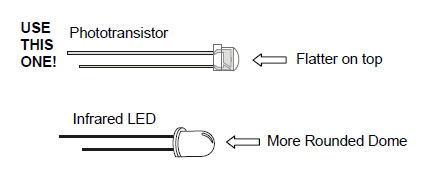
The drawing below will help you tell apart the phototransistor and infrared LED, since they look similar.
Building the Bright Light Detector
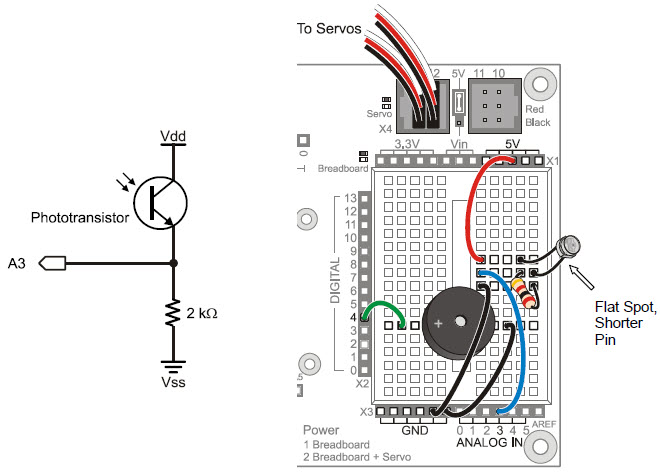
The schematic and wiring diagram below show the schematic and wiring diagram of a circuit very similar to the ones in streetlights that turn on automatically at night. The circuit outputs a voltage that varies depending on how much light shines on the phototransistor. The Arduino will monitor the voltage level with one of its analog input pins.
- Disconnect the battery pack and programming cable from your Arduino, and set the BOE Shield’s switch to 0.
- Remove the whisker circuits, but leave the piezospeaker circuit in place.
- Build the circuit shown, using the 2 kΩ resistor.
- Double-check to make sure you connect the phototransistor’s emitter lead (by the flat spot) to the resistor, and its collector to 5V.
- Also double-check that the phototransistor’s leads are not touching each other.