Activity 6: Testing the Servos
There’s one last thing to do before assembling your BOE Shield-Bot, and that’s testing the servos. In this activity, you will run sketches that make the servos turn at different speeds and directions. This is an example of subsystem testing—a good habit to develop.
Subsystem testing is the practice of testing the individual components before they go into the larger device. It’s a valuable strategy that can help you win robotics contests. It’s also an essential skill used by engineers to develop everything from toys, cars, and video games to space shuttles and Mars roving robots. Especially in more complex devices, it can become nearly impossible to figure out a problem if the individual components haven’t been tested beforehand. In aerospace projects, for example, disassembling a prototype to fix a problem can cost hundreds of thousands, or even millions, of dollars. In those kinds of projects, subsystem testing is rigorous and thorough.
Pulse Width Controls Speed and Direction
This timing diagram shows how a Parallax continuous rotation servo turns full speed clockwise when you send it 1.3 ms pulses. Full speed typically falls in the 50 to 60 RPM range.
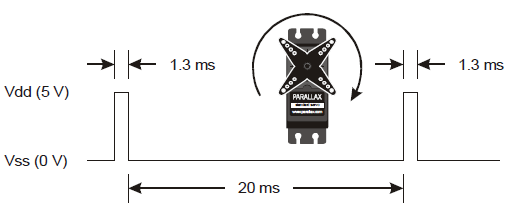
What’s RPM? Revolutions Per Minute—the number of full rotations turned in one minute.
What’s a pulse train? Just as a railroad train is a series of cars, a pulse train is a series of pulses (brief high signals).
Example Sketch: LeftServoClockwise
- Enter, save, and upload LeftServoClockwise.
- Verify that the servo’s horn is rotating between 50 and 60 RPM clockwise.
/*
Robotics with the BOE Shield – LeftServoClockwise
Generate a servo full speed clockwise signal on digital pin 13.
*/
#include <Servo.h> // Include servo library
Servo servoLeft; // Declare left servo
void setup() // Built in initialization block
{
servoLeft.attach(13); // Attach left signal to pin 13
servoLeft.writeMicroseconds(1300); // 1.3 ms full speed clockwise
}
void loop() // Main loop auto-repeats
{ // Empty, nothing needs repeating
}
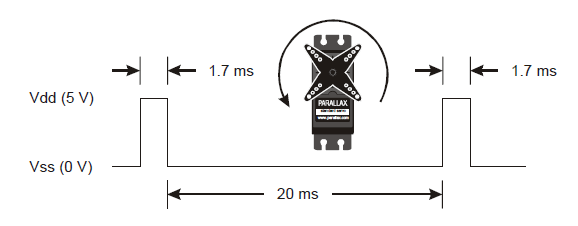
Your Turn: Left Servo Counterclockwise
- Save LeftServoClockwise as LeftServoCounterclockwise.
- In servoLeft.writeMicroseconds, change (1300) to (1700).
- Save the modified sketch and upload it to the Arduino.
- Verify that the servo connected to pin 13 now rotates the other direction, which should be counterclockwise, at about 50 to 60 RPM.
Example Sketch: RightServoClockwise
- Save LeftServoClockwise as RightServoClockwise.
- Replace all instances of servoLeft with servoRight.
- Replace all instance of 13 with 12.
- Run the sketch and verify that the pin 12 servo is rotating between 50 and 60 RPM clockwise.
/*
Robotics with the BOE Shield – RightServoClockwise
Generate a servo full speed clockwise signal on digital pin 12.
*/
#include <Servo.h> // Include servo library
Servo servoRight; // Declare left servo
void setup() // Built in initialization block
{
servoRight.attach(12); // Attach left signal to pin 12
servoRight.writeMicroseconds(1300); // 1.3 ms full speed clockwise
}
void loop() // Main loop auto-repeats
{ // Empty, nothing needs repeating
}
Your Turn – Right Servo Counterclockwise
- In servoRight.writeMicroseconds change (1300) to (1700).
- Save the sketch and upload it to your Arduino.
- Verify that the pin 12 servo turns full-speed counterclockwise, about 50 to 60 RPM.