Introducing the Prototyping Area
The white board with lots of square sockets in it is called a solderless breadboard. This breadboard has 17 rows of sockets. In each row, there are two five-socket groups separated by a trench in the middle. All the sockets in a 5-socket group are connected together underneath with a conductive metal clip. So, two wires plugged into the same 5‑socket group make electrical contact. This is how you will connect components, such as an LED and resistor, to build circuits. Two wires in the same row on opposite sides of the center trench will not be connected.
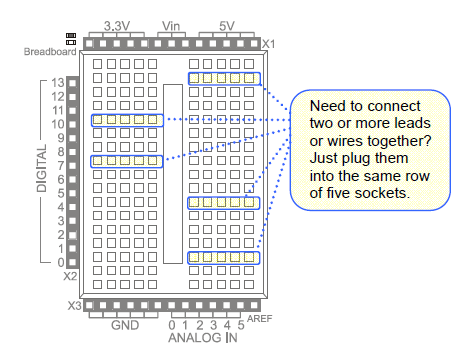
The prototyping area also has black sockets along the top, bottom, and left.
- Top: these sockets have three supply voltages for the breadboard: 3.3 V, Vin (input voltage from either battery pack or programming cable), and 5 V.
- Bottom-left: The first six sockets along the bottom-left are ground terminals, labeled GND; think of them as a supply voltage that’s 0 V. Collectively, the 3.3V, Vin, 5V and GND are called the power terminals, and they will be used to supply your circuits with electricity.
- Bottom-right: The ANALOG IN sockets along the bottom-right are for measuring variable voltages; these connect to the Arduino module’s ANALOG IN sockets.
- Left: The DIGITAL sockets on the left have labels from 0 to 13. You will use these to connect your circuit to the Arduino module’s digital input/output pins.
Digital and analog pins are the small pins on the Arduino module’s Atmel microcontroller chip. These pins electrically connect the microcontroller brain to the board.
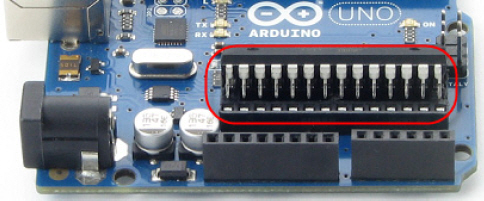
A sketch can make the digital pins send high or low signals to circuits. In this chapter, we’ll do that to turn lights on and off. A sketch can also make a digital pin monitor high or low signals coming from a circuit; We’ll do that in another chapter to detect whether a contact switch has been pressed or released.
A sketch can also measure the voltages applied to analog pins; we’ll do that to measure light with a phototransistor circuit in another chapter.