Introducing the Resistor
Introducing the Resistor
A resistor is a component that resists the flow of electricity. This flow of electricity is called current. Each resistor has a value that tells how strongly it resists current flow. This resistance value is called the ohm, and the sign for the ohm is the Greek letter omega: Ω. (Later on you will see the symbol kΩ, meaning kilo-ohm, which is one thousand ohms.)
This resistor has two wires (called leads and pronounced “leeds”), one coming out of each end. The ceramic case between the two leads is the part that resists current flow. Most circuit diagrams use the jagged line symbol with a number label to indicate a resistor of a certain value, a 470 Ω resistor in this case. This is called a schematic symbol. The part drawing on the right is used in some beginner-level texts to help you identify the resistors in your kit, and where to place them when you build circuits.
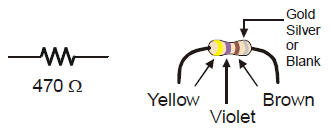
The resistors in your parts kit have colored stripes that indicate what their resistance values are. There is a different color combination for each resistance value. For example, the color code for the 470 Ω resistor is yellow-violet-brown.
There may be a fourth stripe that indicates the resistor’s tolerance. Tolerance is measured in percent, and it tells how far off the part’s true resistance might be from the labeled resistance. The fourth stripe could be gold (5%), silver (10%) or no stripe (20%). For the activities in this book, a resistor’s tolerance does not matter, but its value does.
Each color bar on the resistor’s case corresponds to a digit, as listed in the table below.
| Digit | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| Color | black | brown | red | orange | yellow | green | blue | violet | gray | white |
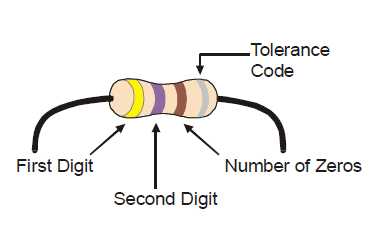
Here’s how to find the resistor’s value, in this case proving that yellow-violet-brown is really 470 Ω:
- The first stripe is yellow, which means the leftmost digit is a 4.
- The second stripe is violet, which means the next digit is a 7.
- The third stripe is brown. Since brown is 1, it means add one zero to the right of the first two digits.
Yellow-Violet-Brown = 4-7-0 = 470 Ω.
Your Turn
- Use the table and picture above to figure out the color code for the 220 Ω resistors you will need for the indicator lights.